Always stay ahead of the weather with EzloPi!
Arduino Nano ESP32 and Rain sensor (Replace Arduino with ESP-based board)
The EzloPi smart devices provide automation through simple, customizable use with our open-source EzloPi platform, making daily life easier and improving human-machine interactions.
Before moving into this example, it is very important to know about the device registration, provisioning and converting the ESP32 device into an EzloPi device along with knowledge of Web Flasher, MiOS Mobile Application for Android/iOS and the MiOS Web Application.
1. About this example
In this project demonstration, we will show you how to convert an existing project into a smart project using the ESP32 development board. The ESP-based EzloPi device provides the capabilities to convert your hardware (projects or devices/sensors) into IoT capable devices.
This following user guide will take you through the steps to make existing Arduino projects into smart projects using ESP MCU based boards. We can get an understanding for this easy process of converting existing or new projects into smart EzloPi projects.
Arduino Nano ESP32 combines the form factor and ease of use of the Arduino Nano with the processing power and wireless capabilities of the ESP32. This combination allows you to create projects that take advantage of the Arduino ecosystem and libraries while also incorporating Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity for various IoT applications. We have demonstrated the Arduino Nano ESP32 as our EzloPi device by interfacing the rain sensor module.
2. Circuit Diagram & Interface
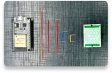
The following components are required for interfacing with the EzloPi device:
From ESP32 (30 pins) to the voltage sensor:
- Arduino Nano ESP32 as an EzloPi smart device.
- LM393 comparator IC module.
- FC-37 rain sensor module.
The wiring diagram of Arduino Nano ESP32 is represented as follows:
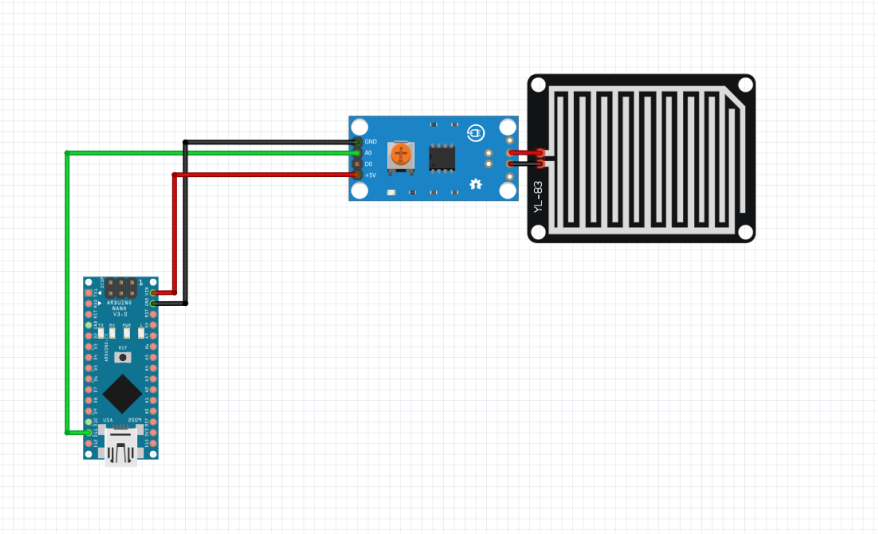
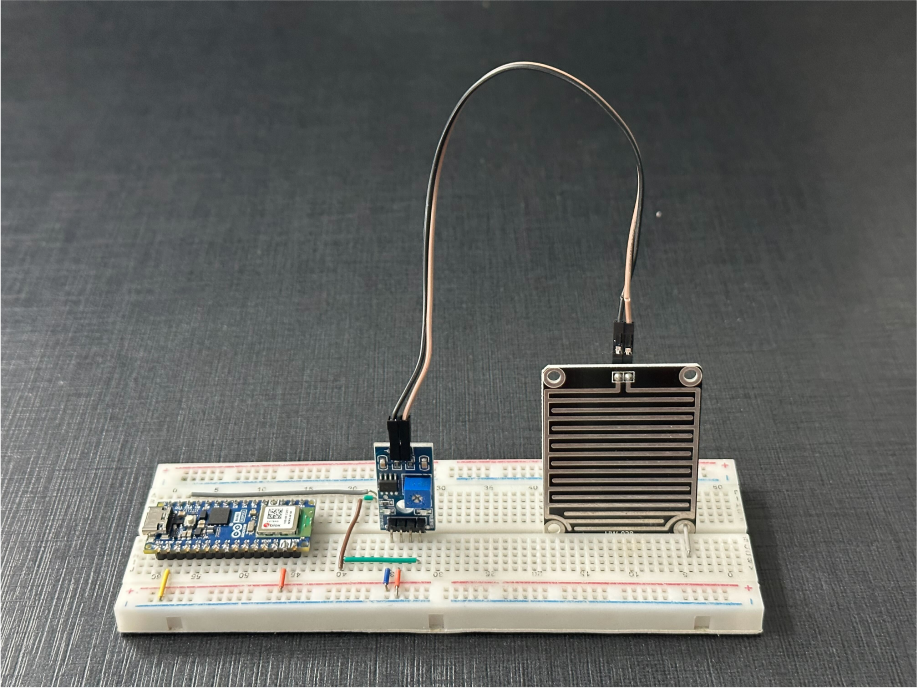
The following connections are made in order to complete the entire circuit setup.
From Arduino Nano ESP32 to the LM393 comparator module:
- Connect the VCC of the Arduino Nano ESP32 with the VCC of the LM393 module.
- Connect the GND pin of the Arduino Nano ESP32 to the GND pin of the LM393 module.
- Connect theArduino Nano ESP32’s GPIO D11 pin to the A0 of the module.
From the LM393 module to the Rain Sensor:
- Connect any of the output pins of the rain sensor to the positive and negative terminal of the comparator module respectively.
3. Interfacing the Rain Sensor with the EzloPi Web Flasher:
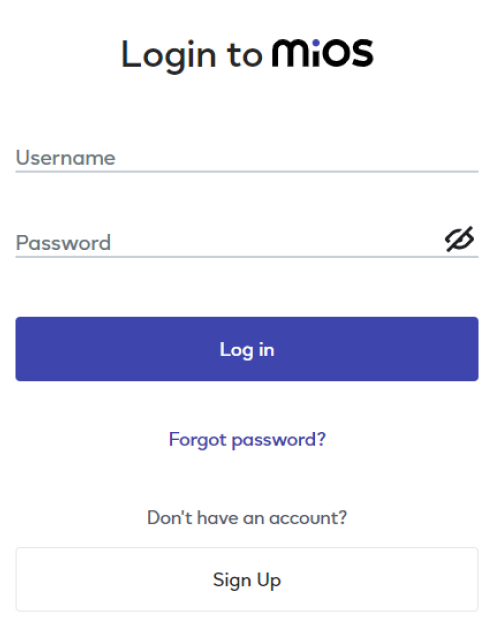
1. Set up your device/hardware by visiting config.ezlopi.com

- Log in using the credentials which you just set earlier while signing up.
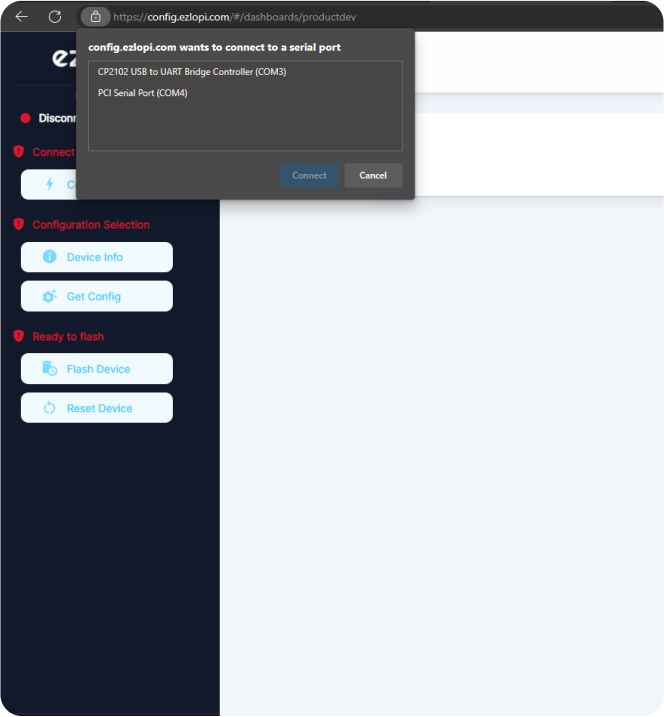
- Now, click on the Connect Device button and a pop-up window will appear.

Now, select COM Port to which your ESP32 device is connected. In our case, the COM3 port is used.
Click Connect.
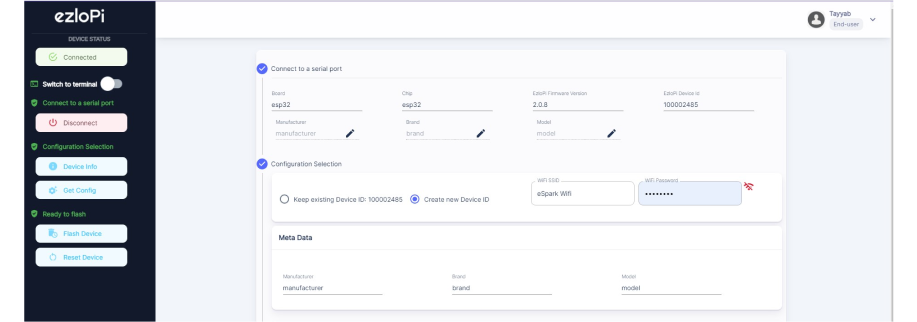
- If you are new to this and it's your first time configuring, select Create new Device ID. Enter Wifi SSID and Wifi Password.
- In the Device Configuration, tab click on Analog Output.
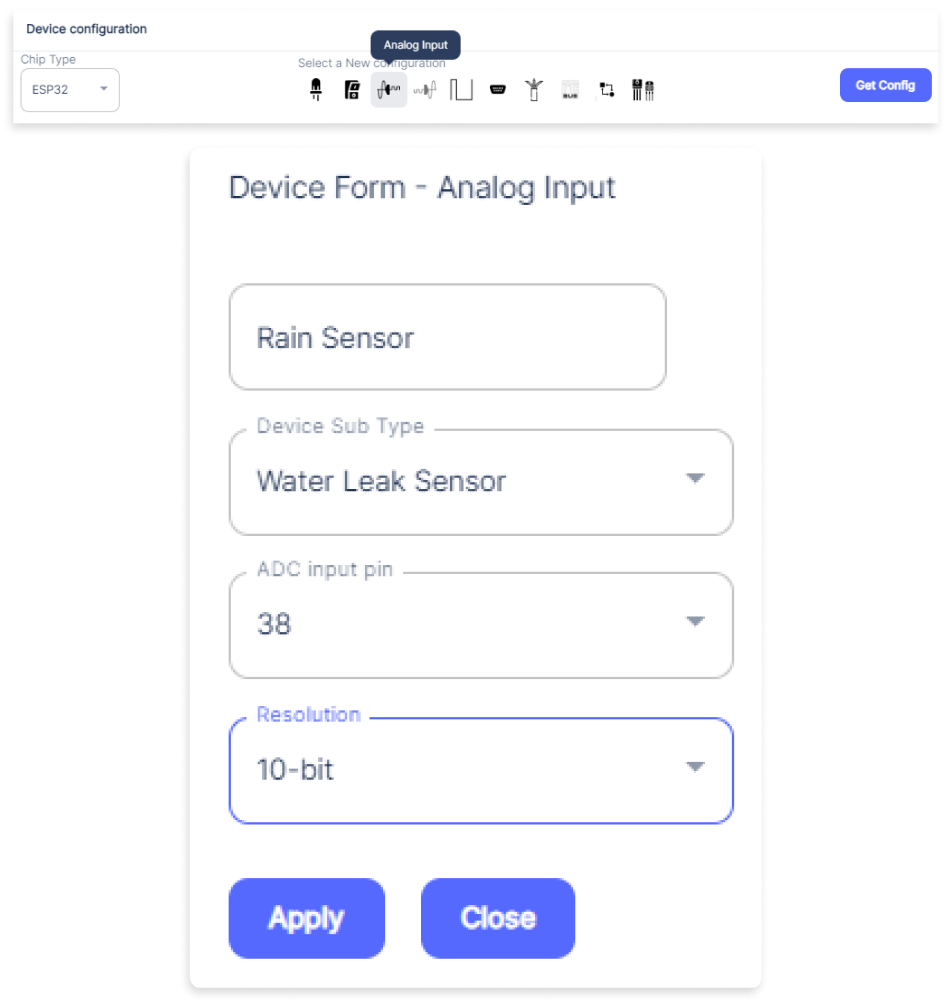
- An Analog Input window will open for inputting the following parameters:
- Set a device name of your choosing. In our case, we set it to Rain Sensor.
- Set device Subtype to Water leak Sensor.
- Set the ADC input pin to 38.
- Set the Resolution to 10-bit.
- Now Click the Apply button.
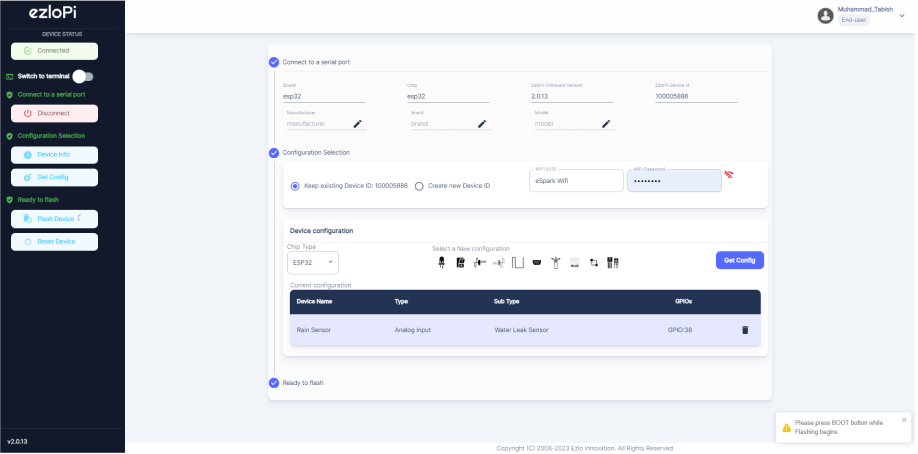
- After clicking the apply button you can see a table of your setting in the device configuration tab.
- Press the Flash Device button.
- A window will appear on the bottom right side of the screen displaying “Please press BOOT button while flashing begins.”
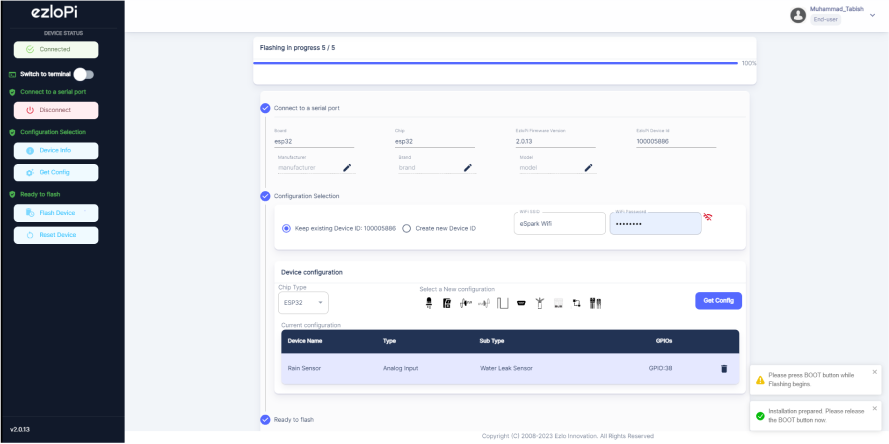
- Hold the BOOT button down until the next window appears on the bottom right side of the screen which says “Installation prepared. Please release the boot button now.”
- Release the BOOT button from your ESP32 when this pop-up on the bottom right window appears.
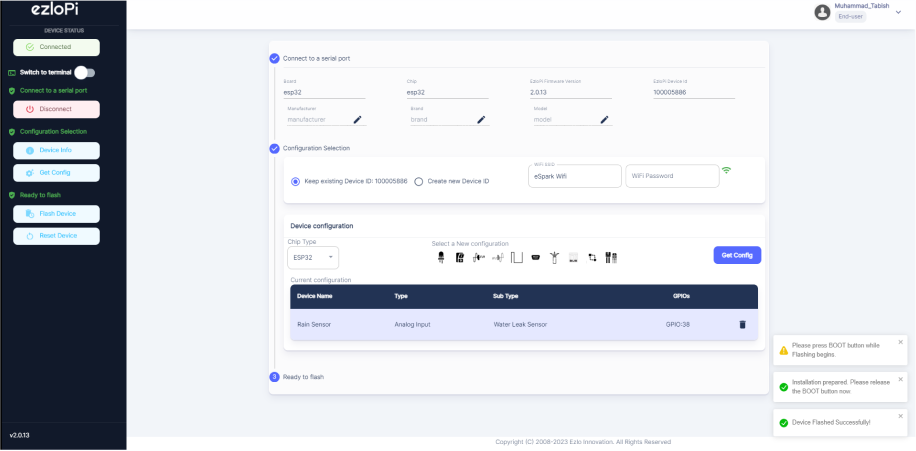
- After some time, a popup will appear saying Device Flashed Successfully! This means that your device has been set up successfully.
4. MiOS App
You can download the MIOS Android app from the Google Play Store and Apple App Store.
- After downloading the app, proceed to install the application and open it.

- Using the MIOS mobile application, create a new Ezlo Cloud account using the sign-up option. If you already have an account, you may proceed to log in.

- After successfully logging in, you will be able to see the number of controllers connected such as a lamp, fan, or any other device in the MiOS app. Tap on any controller of your desired ID:
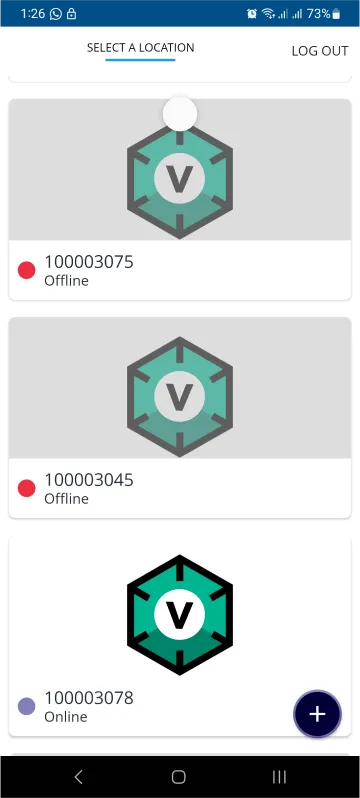
- You will be able to see the status of your controller whether it is online or offline. Access the device dashboard, and tap the device. The following view of the dashboard will appear:
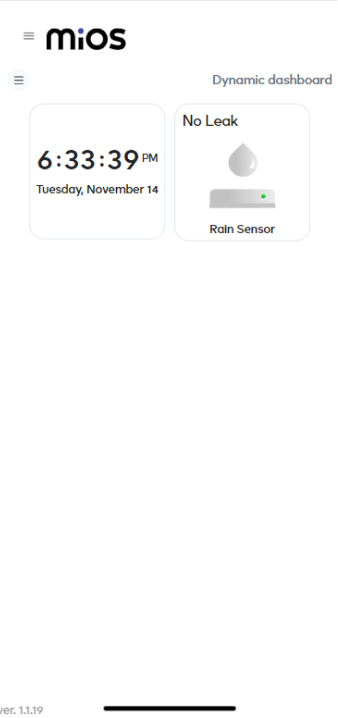
- After opening the dashboard, you will be able to see the tile of your connected device.
- As you can see in the example given above, we can see the rain sensor tile. It shows a “No Leak” message on the tile as the sensor is not detecting any raindrops or rain water.
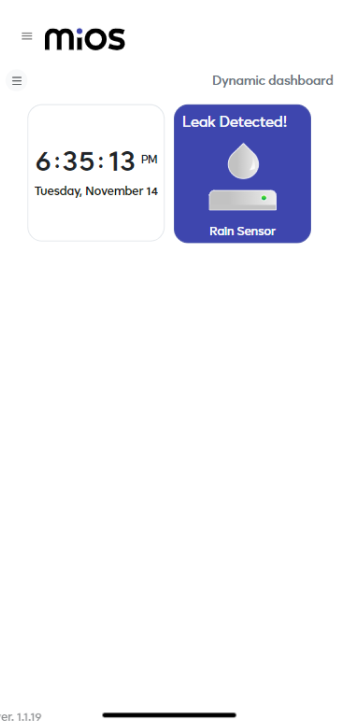
- Similarly ,it shows a “Leak Detected” message on the tile when the sensor is detecting any raindrops or rain water.
5. MiOS Web Application
- After configuring the controller with the EzloPi web flasher, head to ezlogic.mios.com

- Use the same credentials to log in that you used for configuring the controller with the web flasher.
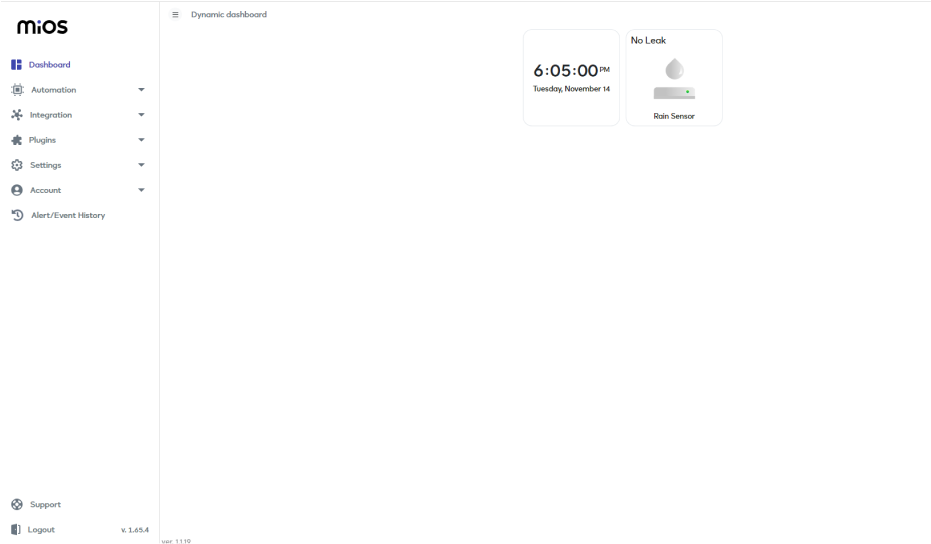
- Now, you will see a tile labeled as rain sensor on the MiOS web application dashboard. Currently, no rain drops are detected by the sensor therefore the rain sensor tiles show the “No Leak” message.
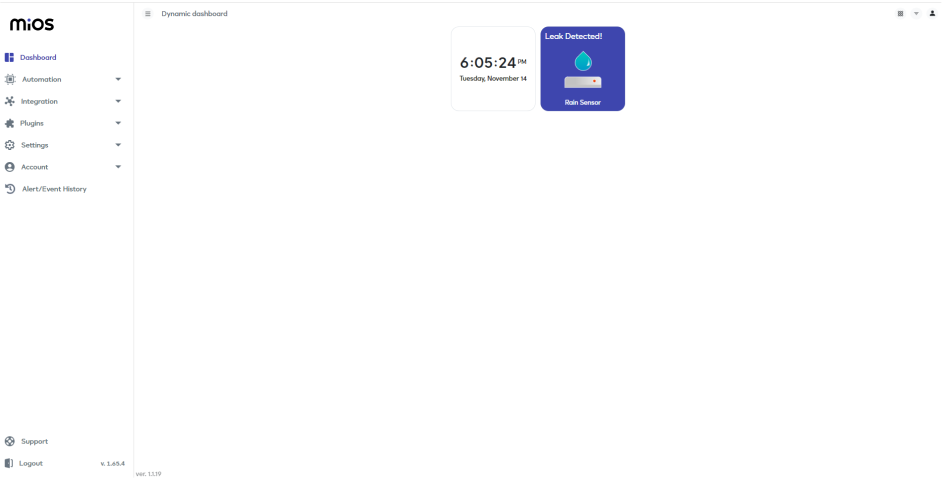
- Similarly ,it shows a “Leak Detected” message on the tile when the sensor is detecting any raindrops or rain water.

eZlopie Products A single-channel 5V relay module $00.00

eZlopie Products Momentary switch $00.00

eZlopie Products Level Shifter Module (BSS138) $00.00

eZlopie Products ESP32
$00.00

eZlopie Products AC Lamp and Holder
$00.00